软件架构期末复习
The types, concepts, and tactics of OAs.
type
一共有3类质量属性:系统的质量属性、受架构影响的商业属性、与架构本身相关的一些质量属性
重点讨论系统的质量属性:可用性、可修改性、性能、安全性、可测试性和易用性
1. 可用性 Availability
- 可用性是指软件具备在需要时准备好执行任务的特性。
- the ability of a system to mask or repair faults such that the cumulative service oiutage period does not exceed a required value over a specified time interval.
- is about minimizing service outage time by mitigating faults(减轻故障).
- 关注内容:
- 如何检测系统故障
- 系统故障发生的频度
- 出现故障时会发生什么情况
- 允许系统有多长事件非正常运行
- 什么时候可以安全地出现故障
- 如何防止故障的发生以及发生故障时要求进行那种通知
定义:系统正常运行的时间比例
可用性的一般场景:
- 刺激源 / Stimulus source:刺激源分为外部和内部、对应刺激源的响应是不同的。
- 刺激 / Stimulus:可能会发生的错误
- 疏忽 / Neglect
- 崩溃 / Crash
- 时间 / Timing
- 响应 / Response
- 制品 / Artifact:指定了要求具有极高可用性的资源:处理器、通信通道、进程或储存
- 环境 / Environment:当出现错误、故障时,系统的状态会影响期望的系统响应。
- 响应 / Response:在出现系统故障时,对错误进行捕捉处理
- 响应量度 / Response measure:系统必须可用的时间间隔
Availability Tactics 可用性策略
- Goal:
- Availability Tactics enable a system to endure faults so that services remain compliant with their specifications.
- The tactics keep faults from becoming failures or at least bound the effects of the fault and make repair possible.
- Tactics Tree: 可用性的策略树有五个分支:输入错误、检测故障、从故障中恢复、防范故障、输出结果。
- 输入错误
- Detect Faults:Ping&Echo, Monitor, Heartbeat, Timestamp, Sanity Checking 完整性检查, Condition Monitoring, Voting, Exception Detection, Self-Test
- Recover from Faults:
- Preparation, Reintroduction and Repair: Active Redundancy, Passive Redundancy, Spare, Exception Handling, Rollabck, Software Update, Retry, Ignore Faulty Behavior, Degradation, Reconfiguration
- Reintroduction: Shadow, State Resynchronization, Escalating Restart, Non-Stop Forwarding
- Prevent Faults: Removal from Service, Transactions, Predictive Model, Exception Prevention, Incrase Competence Set
- Output: Fault Masked or Repair made
Detect Faults: 故障检测
- Ping&Echo: 检查网络可达性以及测量通过相关网络路径的往返延迟。
- Monitor: 监控组件用于检测系统的其他部分的健康状态
- Heartbeat: 系统监控器与被监控进程之间的周期性消息交换
- Timestamp: detect incorrect sequences of events, particularly in distributed message-passing systems
- Condition Monitoring: The process of checking the conditions of a device or process, or validating assumption make during design
- Checksum: used in data storage and transmission to ensure the integrity of the data
- voting: the common realization of this tactic is Triple Modular Redundancy (TMR)
Recover from Faults(Preparation & Repair)
- Active Redundancy:
- Spare
- Warm Spare
- Rollback
- Retry
- Ingnore Faulty Behavior 鸵鸟算法
- Degradation: 保持最关键的系统功能,同时丢弃较不重要的功能
Prevent Faults
- Removal from Service
- Transactiosn 事务:Transaction bundle state updates to ensure that asyncchronous messages exchanged between distributed components are
- Atomic: 原子的
- Consistent 事务中不会使得系统出现不一致的状态
- Isolated 事务之间是隔离的
- Durable 事务是持久的
- Predictive Model: 预测模型在检测到可能导致未来出现故障的条件时,采取纠正措施
- Increase Competence Set
2. 可修改性 Modifiability
concept
Modifiablity is about change and our interest in it is in the cost and risk of making changes.
- 关注内容
- 可以修改什么
- what is the likelihood of the change
- 何时进行变更以及由谁进行变更
- what is the cost of the change
可修改性的一般场景:
- 刺激源:规定由谁来进行改变(开发人员、系统管理员、最终用户)
- 刺激:这部分指定了要进行的改变:增删改功能、优化系统质量、提高可用性
- 制品:指定要对什么进行改变:系统的功能、平台、用户界面、环境或者与之操作的另一个系统
- 环境:指定了什么时候可以进行改变(设计、编译、构建、启动、运行)
- 响应:理解如何改变、然后进行改变、测试和部署。
- 响应度量:根据所影响的元素的数量度量的成本、努力、资金;该修改对其他功能或质量属性所造成的影响的程度。
tactics
Goal
- controlling the complexity of making changes
- controlling the time and cost to make changes
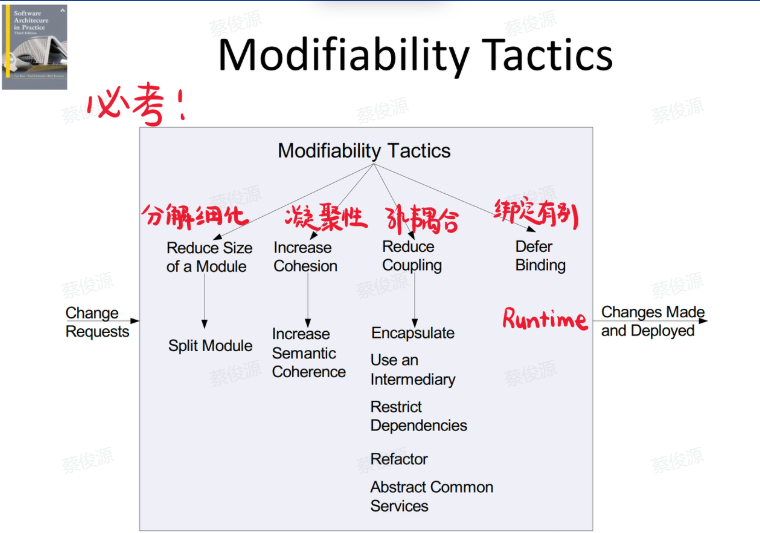
Tactics Tree(必考)
Reduce Size of a Module
• Split Module: If the module being modified includes a great deal of capability, the modification costs will likely be high. • 拆分模块:如果被修改的模块包含大量功能,则修改成本可能会很高。 • Refining the module into several smaller modules should reduce the average cost of future changes. • 将模块细化为几个较小的模块应该可以降低未来更改的平均成本。
Increase Cohension
模块中的职责A和职责B不为同一个目的而服务,那么他们应该被划分到不同的模块。
Reduce Coupling
- What is coupling: A model’s dependence of other models.
- If two modules’s responsibilities overlap, a single change may affect them both.
- Coupling i smaasured by this overlap(重叠)(即对一个模块的修改会传播到另一个模块的概率)
- High coupling is an enemy of modifiability.
措施:
- Encapsulate:封装,通过隐藏模块的内部细节,可以减少模块之间的耦合。
- Intermediary:中间件,打破模块之间的直接联系,通过引入一个中间件,可以减少模块之间的耦合。
- Restrict Dependencies:限制依赖
- Abstract Common Services:抽象公共服务,通过提供一个抽象的接口,可以减少模块之间的耦合。常见于cpp中的虚父类声明公共服务接口,rust中的trait也有相同的作用。
几个常见的异步模型:
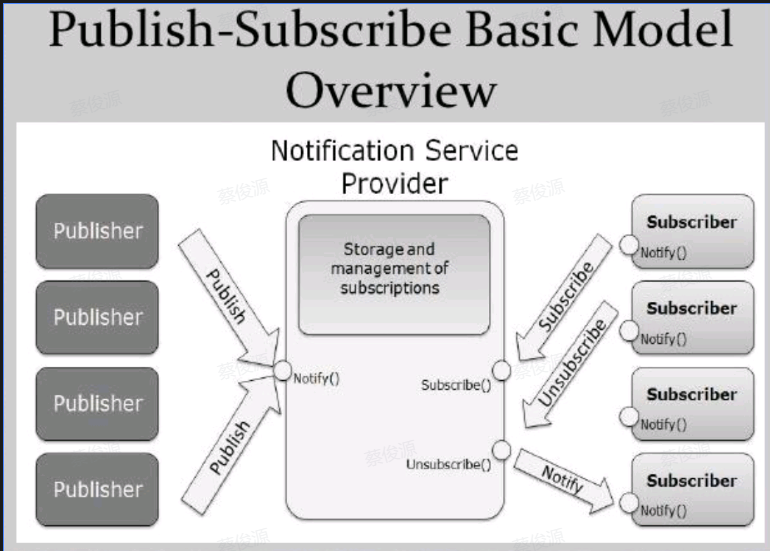
Pub-Sub Mode
P2P Mode
Key Functions Implemented by P/S Middleware Service
- Event Filtering :据特定的条件或规则筛选事件,以便只将感兴趣的事件传递给订阅者
其实就是将发送给publisher的事件进行分类,订阅者在订阅时选择关心的事件类别,publisher在监听到事件到来的时就会先判断事件类别,然后选择性的调用notify。可以按主题分类Topic-based,也可以按内容分类Content-based。
优点:
- Highly suited for mobile applications, ubiquitous computing, and distributed embedded systems. / 非常适合用于移动应用、普适计算和分布式嵌入式系统。
- Robust - Failure of publishers or subscribers does not bring down the entire system. / 强健性 - 发布者或订阅者的失败不会导致整个系统崩溃。
- Scalability - Suited to build distributed applications consisting of a large number of entities. / 可扩展性 - 适用于构建由大量实体组成的分布式应用。
- Adaptability - Can be varied to suit different environments (mobile, internet games, embedded systems, etc.). / 适应性 - 可以根据不同的环境(如移动、互联网游戏、嵌入式系统等)进行调整。
缺点:
- Reliability - No strong guarantee on broker to deliver content to subscriber. After a publisher publishes the event, it assumes that all corresponding subscribers will receive it. / 可靠性 - 经纪人无法强有力地保证将内容传递给订阅者。在发布者发布事件后,它假设所有相关订阅者都会接收到事件。
Potential bottleneck in brokers when subscribers and publishers overload them. (Solve by load balancing techniques) / 当订阅者和发布者过载时,经纪人可能成为潜在的瓶颈。(通过负载均衡技术解决)
- Event Routing: 事件路由,将事件传递给订阅者
3. 性能 Performance
concept
性能与时间有关,事件发生时,系统必须对其做出响应。性能与将要耗费系统多长时间做出响应有关。
性能的一般场景:
- 刺激源:来自外部或内部。
- 刺激:事件的到来。
- 制品:系统的服务。
- 环境:正常模式、超载模式
- 响应:处理刺激:改变服务级别
- 响应度量:系统处理到达事件所用的时间(等待时间或必须处理的事件的期限)、该时间的变化(抖动)、在某一特定时间间隔内可以处理的事件数量(吞吐量)或对不能处理的事件的描述。(缺失值、数据丢失)
tactics
Goal
- to generate a response to an event arriving at the system within some time-based constraint.
- The event can be single or a stream, and is the trigger to perform computation
Categories / 类别
Control resource demand / 控制资源需求
- To produce smaller demand on the resources / 产生对资源的较小需求
- Operate on the demand side / 在需求侧操作 Manage resources / 管理资源
- To make the resources at hand work more effectively in handling the demands / 使手头的资源在处理需求时更有效地工作
- Operate on the response side / 在响应侧操作
Resources / 资源
- Hardware resources / 硬件资源: e.g., CPU, data stores, network bandwidth, and memory. 硬件资源:例如 CPU、数据存储、网络带宽和内存。
- Software resources / 软件资源: e.g., buffers, or critical sections. 软件资源:例如缓冲区或关键区段(critical sections)。
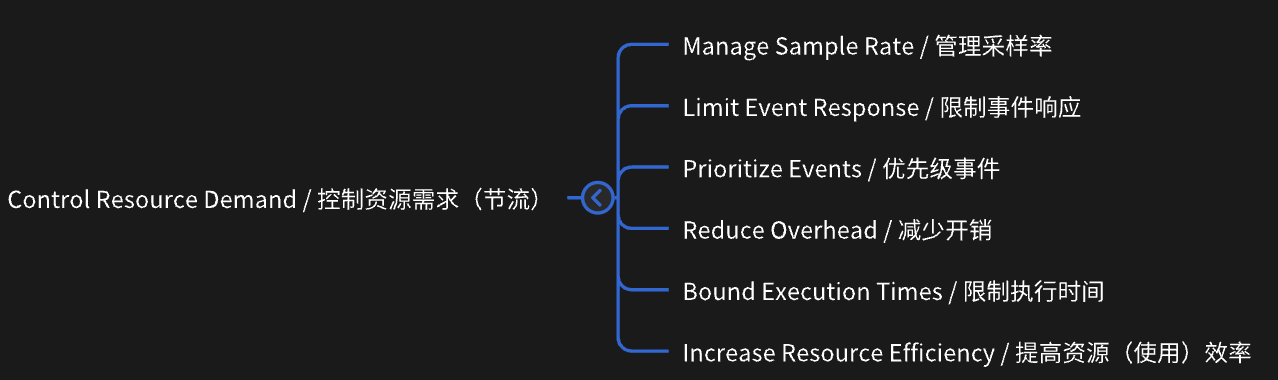
Tatics Tree(开源节流)
- 节流 控制资源需求
Manage Sample Rate
- Objective: To reduce the sampling frequency at which stream of data is captured, helping to minimize unnecessary data processing and system load
减少对捕捉到的数据流的采样频率,有助于减少不必要的数据处理和系统负载
Prioritize Events
- Objective: To impose a priority scheme that ranks events according to their importance. Low-priority events are ignored when system resources are insufficient. 目标:制定优先级方案,根据事件的重要性对其进行排序。当系统资源不足时,忽略低优先级事件。
Reduce Overhead
- Objective: The use of intermediaries (such as proxies or message brokers) increases the resources consumed in processing an event stream. Removing these intermediaries can improve latency.
目标:中介的使用(如代理或消息中间件)会增加处理事件流所消耗的资源,去除中介可以改善延迟。
- Trade-off: There is a trade-off between modifiability (flexibility of the system) and performance (efficiency of event processing).
权衡:在可修改性(系统灵活性)和性能(事件处理效率)之间存在权衡。
Bound Execution Times
- Objective: Place a limit on how much execution time is used to respond to an event, preventing long-running tasks from blocking the system. 目标:限制响应事件所用的执行时间,防止长期运行的任务阻塞系统。
- In algorithm design, limiting the number of iterations is one method for bounding execution time. 在算法设计中,限制迭代次数是限制执行时间的一种方法。
Increase Resource Efficiency
- Objective: Improving the algorithms used in critical areas will decrease latency and increase the overall resource efficiency of the system. 目标:改进关键领域中使用的算法将减少延迟,并提高系统的整体资源效率。
To reduce the complexity of the algorithm / 降低算法复杂度: Simplifying algorithms can help to reduce the time and resources required for processing, improving system performance. 简化算法有助于减少处理所需的时间和资源,从而提高系统性能。
- 开源 管理资源

Increase Resources
- Objective: To reduce latency by upgrading system resources. 目标:通过升级系统资源来减少延迟。
- Faster Processors / 更快的处理器
- Additional Processors / 增加处理器
- Additional Memory / 增加内存
- Faster Networks / 更快的网络
Increse Concurrency
Objective: To reduce blocked time by processing tasks in parallel, improving overall system performance. 目标:通过并行处理任务来减少阻塞时间,从而提高系统整体性能
Parallel Processing of Requests / 请求的并行处理: If requests can be processed in parallel, the system can handle multiple tasks simultaneously, reducing waiting time and improving throughput. 如果请求可以并行处理,系统就能同时处理多个任务,减少等待时间并提高吞吐量。
Concurrency through Threads / 通过线程引入并发: Concurrency can be introduced by processing different streams of events on different threads, allowing independent processing of multiple event streams. 通过在不同线程上处理不同的事件流,可以引入并发,允许多个事件流的独立处理
Maintain Multiple Copies of Computations 服务冗余处理
- The purpose of replicas is to reduce resource contention on a single server. / 副本的目的是减少单个服务器上的资源争用。
- Load balancer assigns new work to one of the duplicate servers. / 负载均衡器将新工作分配给其中一个副本服务器。
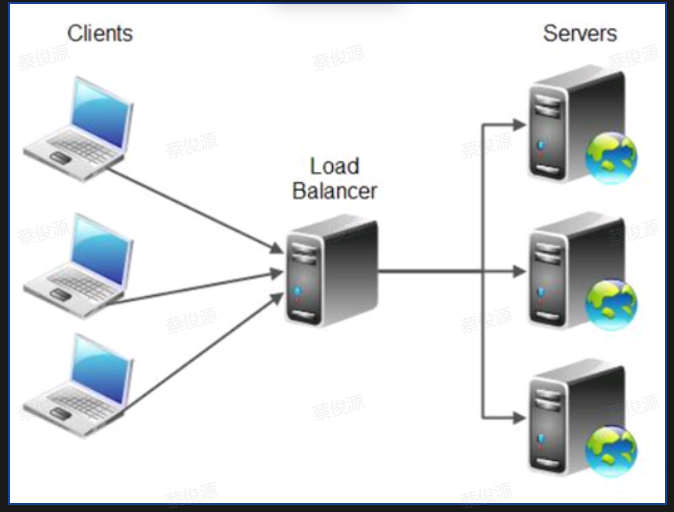
Maintain Multiple Copiies of Data 数据冗余处理
Data Caching 数据缓存
Definition: Data caching involves storing copies of data on storage devices with varying access speeds (e.g., memory vs. disk, or local vs. remote access via networks). 定义:数据缓存是将数据的副本存储在具有不同访问速度的存储设备上(例如,内存访问与磁盘访问,或通过网络的本地访问与远程访问)。
Memory Access vs. Disk Access / 内存访问与磁盘访问: Memory access is much faster than disk access, so frequently used data can be cached in memory to reduce access time. 内存访问比磁盘访问快得多,因此频繁使用的数据可以缓存到内存中,以减少访问时间。
Local Access vs. Remote Access / 本地访问与远程访问: Accessing data locally (from the same machine) is faster than accessing data remotely over a network, so caching frequently used data locally can reduce network delays. 本地访问(来自同一台机器)比远程通过网络访问数据更快,因此将频繁使用的数据缓存到本地可以减少网络延迟。
Data Replication
Definition: Data replication involves maintaining separate copies of data in different locations to reduce contention from multiple simultaneous accesses. This improves both availability and performance. 定义:数据复制是保持数据在不同位置的副本,以减少多次并发访问时的竞争,从而提高可用性和性能。
Reducing Contention / 减少竞争: By replicating data, different users or processes can access separate copies of the data simultaneously, improving system performance and reducing delays. 通过复制数据,不同的用户或进程可以同时访问数据的独立副本,从而提高系统性能并减少延迟。
Scheduling 调度问题
当资源发生竞争时,必须进行资源调度以确保公平且高效的资源分配,需要解决处理器调度、缓存区调度和网络调度的问题。
Resource Model / 资源模型
- The resources include a set of machines/processors which are connected by networks. / 资源包括一组由网络连接的机器 / 处理器
- Machine / Processor Model / 机器 / 处理器模型
- Processing capability / speed, energy comsumption / 加工能力/速度、能耗
- Network model / 网络模型
- Network topology / 网络拓扑
- Bandwidths / 带宽
- Messages and energy comsumption / 信息和能量消耗
- e.g. Sensor networks, Data Center networks, Mobile Cloud / 例子:传感器网络,数据中心网络,移动云
Objectives 目标
- Minimize completion time
- Meeting deadlines
- Maximize throughput …
Classification of Scheduling 调度分类 Real time scheduling v.s. non-real time scheduling / 实时调度与非实时调度
Static scheduling v.s. dynamic scheduling / 静态调度与动态调度
Offline scheduling v.s. online scheduling / 离线调度与在线调度
Determinist scheduling v.s. Stochastic scheduling / 确定性调度与随机调度
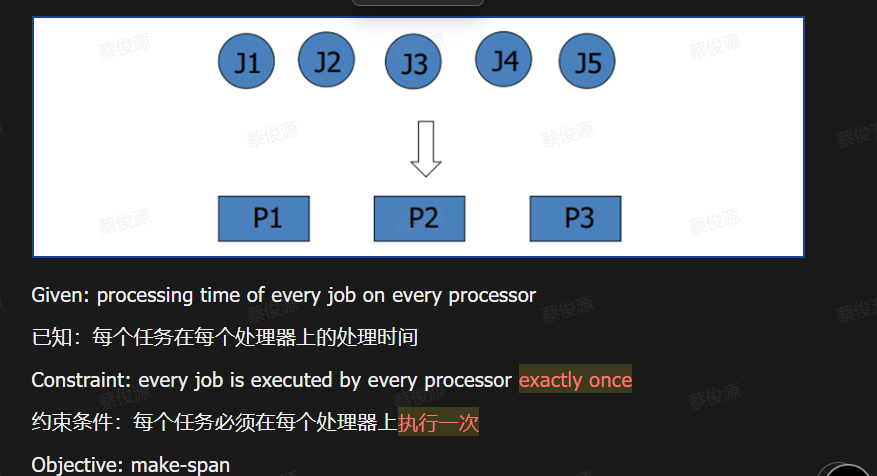
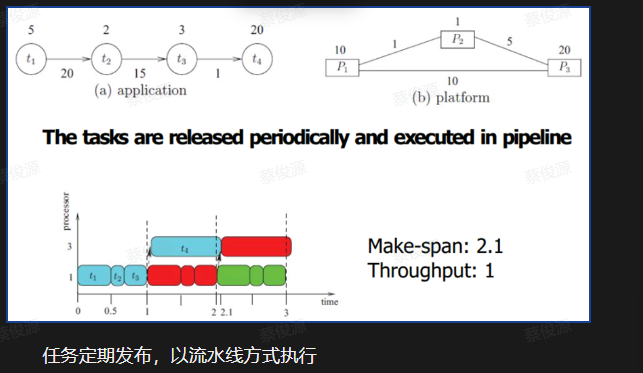
Task Scheduling Problems 任务调度问题
- 单处理器上的批量任务调度
- 多处理器上的批量任务调度
- Given: release time, workload of each task 已知:每个任务的释放时间、工作量
- To determine where and when each task is executed 目的是确定每个任务的执行位置和时间
- Objectives: make-span 目标:完成时间(Make-span)
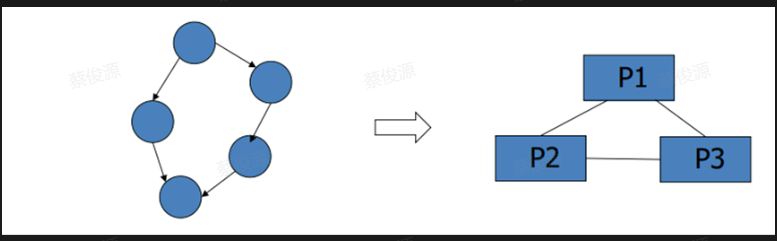
- 异构处理器上的有向无环图调度
- Job shop scheduling 作业车间调度
- Periodic tasks scheduling 周期性任务调度
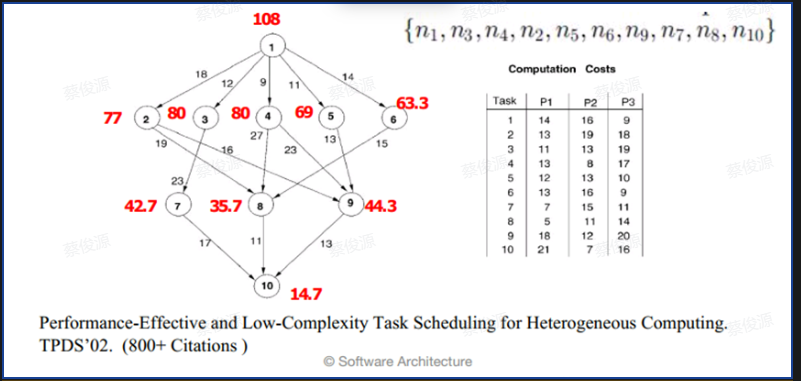
List Scheduling Method 列表调度方法
Step1:Task Selection
Upward Rank
图片解释: 左手边箭头上的数字是路径时间,右手边一个表是Task 1-10 在异构的处理器 P1-3 上对应的计算时间,红色字等于max(上一节点计算时间+上一节点到本节点的路径时间)+average(本节点在P1-3上的平均计算时间),为什么要max,因为本节点的上一个节点可能有多个,即本节点可以指向多个节点。那计算出来的这个红色字有什么用呢?
Step2:Processor Selection
- Earliest Finish Time / 最早完成时间
- For each task, select the machine which can finish that task in the earliest time. / 对于每个任务,选择能够在最早时间完成该任务的机器。
这个有向无环图的构建方法是自底向上构建。需要计算每个任务在各个异构处理器上计算的平均时间,从最后一个任务开始,该任务的红色字为平均时间。然后计算上一节点的红色字:max(上一节点红色字+路径时间)+average(本节点在P1-3上的平均计算时间)
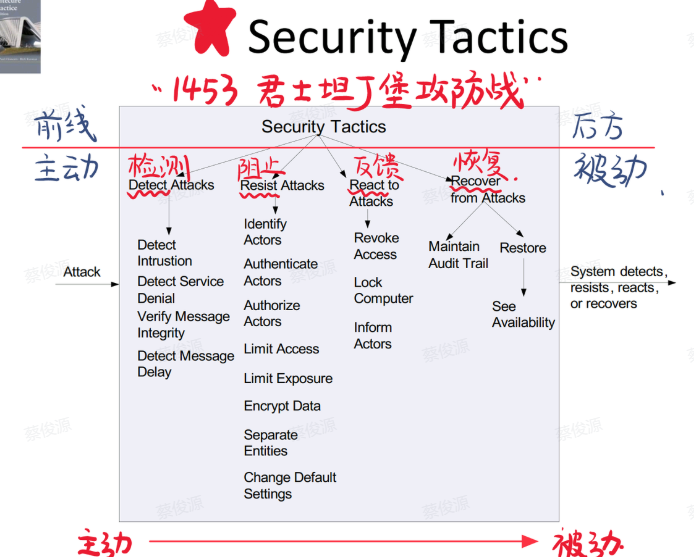
4. 安全性 Security
concept
安全性是衡量系统在向合法用户提供服务的同时,阻止非授权使用的能力。
安全性的一般场景:
- Source:攻击源是人或者另一个系统。
- Stimulus:攻击或试图违反安全性。
- Artifact:攻击的目标可能是系统提供的服务、也可能是系统中的数据、可能是系统的组件或资源,或者让系统产生或消耗数据。
- environment:在线或离线;联网或断网;有防火墙或没有防火墙
- response:对用户进行身份验证、隐藏用户的身份;阻止对数据和服务的访问;
- response measure:用成功的概率表示、避开安全防御措施所需要的时间、努力、资源;检测攻击的可能性;
tactics
- Detect Attack
- Detect Intrusion / 检测入侵
- Detect Service Denial / 检测服务拒绝
- Verify Identity / 验证身份
- Detect Message Delay / 检测消息延迟
- Resist Attack
- React to Attack
- Recover from Attack
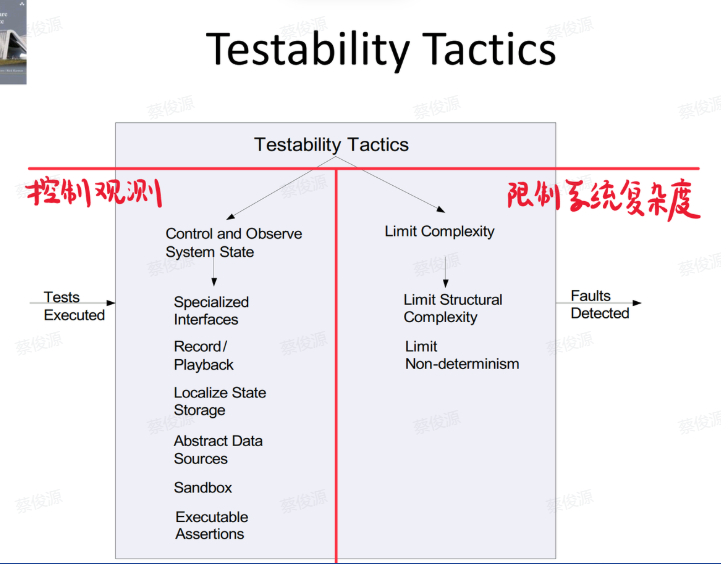
5. 可测试性 Testability
concept
通过测试揭示软件缺陷的容易程度。
可测试性的一般场景:
- 刺激源:单元开发人员、增量集成人员、系统验证人员、客户验收人员、系统用户
- 刺激:已完成的分析、架构、设计、类和子系统集成;所交付的系统
- 制品:设计、代码段、完成的应用
- 环境:设计时、开发时、编译时、部署时
- 响应:提供对状态值的访问、提供所计算的值、准备测试环境
- 响应度量:一致性的可执行语句的百分比、如果存在缺陷出现故障的概率、测试用例的数量、测试用例的覆盖率
tactics
Goal 可测试性策略的目标是允许在软件开发增量完成后更容易地进行测试。
Tactics Tree(必考)
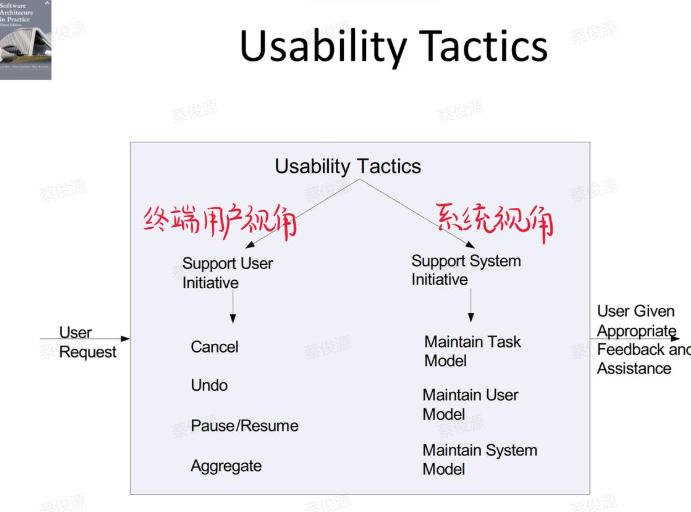
6. 易用性 Usability
易用性关注的是对用户来说完成某个期望任务的容易程度和系统所提供的用户支持的种类。
易用性的一般场景:
- 刺激源:最终用户
- 刺激:最终用户想有效地使用系统,学习使用系统、把错误的影响减到最小,适配系统或对最低的一个示例。
- 制品:系统
- 环境:易用性所涉及的用户从是在运行时或系统配置时发生。
- 响应:系统应该为用户提供所需要的特性,或预计到用户的需要。
- 响应度量:用户学习系统所需的时间、用户在使用系统时所需的时间、用户在使用系统时所需的努力、用户在使用系统时所需的资源。
tactics
7. Interoperability 互操作性
concept
Interoperability is about the degree to which two or more systems can usefully exchange meaningful information via interfaces in a particular context./ 互操作性是指两个或多个系统在特定上下文中通过接口有效地交换有意义的信息的程度。
Seenario
| Portion of Scenario / 场景中的组成部分 | Possible Values / 可能的取值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source / 源头 | A System一个系统 | |||
| Stimulus / 激励 | A request to exchange information among system(s)系统间交换信息的请求 | |||
| Artifact / 组件 | The systems to exchange information among system(s)系统间交换信息的系统 | |||
| Environment / 环境 | System(s) wishing to interoperate are discovered at run time or known prior to run time希望互操作的系统在运行时被发现或在运行之前已知 | |||
| Response / 反馈 | One or more of the following:以下之一或多个:The request is (appropriately) rejected and appropriate entities (people or systems) are notified. 请求被(适当地)拒绝,相关实体(人员或系统)被通知。The request is (appropriately) accepted and information is exchanged successfully. 请求被(适当地)接受,信息成功交换。The request is logged by one or more of the involved systems. 请求被一个或多个相关系统记录。 | |||
| Response Measure / 反馈度量 | One or more of the following:以下之一或多个:Percentage of information exchanges correctly processed 正确信息交换的百分比Percentage of information exchanges rejected 被拒绝的信息交换的百分比 | Portion of Scenario / 场景中的组成部分 | Possible Values / 可能的取值 |
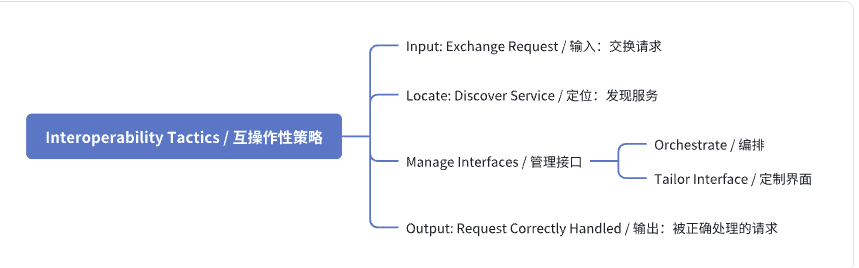
tactics tree
Goal
For two or more systems to usefully exchange information they must / 两个或多个系统要有效地交换信息,它们必须
- Know about each other. That is the purpose behind the locate tactics, / 了解彼此。这是定位策略背后的目的,
- Exchange information in a semantically meaningful fashion. That is the purpose behind the manage interfaces tactics. / 以语义上有意义的方式交换信息。这是管理接口策略背后的目的。Two aspects of the exchange are / 交换的两个方面是
- Provide services in the correct sequence. / 提供正确的服务顺序。
- Modify information produced by one actor to a form acceptable to the second actor. / 将一个参与者产生的消息修改为第二个参与者可以接受的形式。
Locate
Service DISCOVERY / 服务发现
- UDDI for Web Services(Universal Description, Discovery, and Integration) / 用于Web服务的UDDI(通用描述、发现和集成)
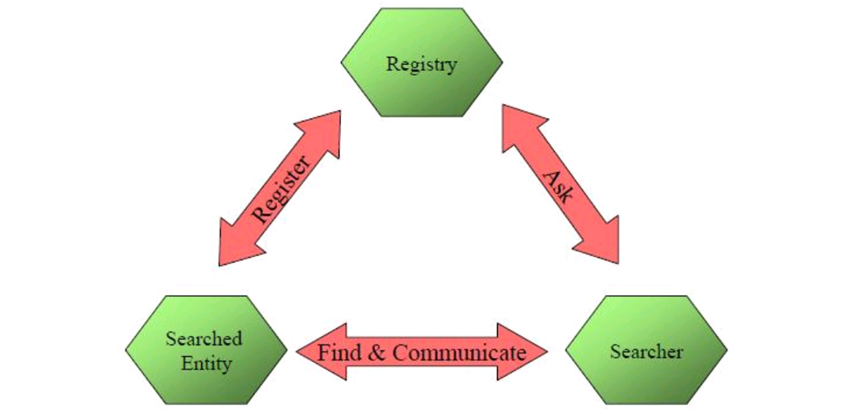
**Searching Method - Registration ** Introduction of the “Middlemen”, Registry / “中介”介绍,注册表
- The searched entity registers to a registry / 被搜索的实体向注册表注册
- The searcher can address the registry to get information and find the searched entity / 搜索者可以查询注册表以获取信息并找到被搜索的实体
Example
- Service providers register their web services at UDDI registry which can be searched and found by Service Requestors / 服务提供者将其Web服务注册到UDDI注册表,服务请求者可以在该注册表中搜索并找到这些服务。
Manage Interfaces
Orchestrate / 协调
- Uses a control mechanism to coordinate, manage, and sequence the invocation of services. / 使用控制机制来协调、管理和按顺序调用服务。
- Orchestration is used when systems must interact in a complex fashion to accomplish a complex task. / 协调用于当系统必须以复杂的方式相互作用以完成复杂任务时。 Tailor Interface / 定制接口
- Add or remove capabilities to an interface such as translation, buffering, or data-smoothing. / 向接口添加或删除功能,如翻译、缓冲或数据平滑处理。
问题:
- Availability and related tactics (e.g., how to detect faults?)
背质量属性的scene和tatics tree
- Performance and related tactics
就是需要知道各种质量属性的理念和相关策略
Architectural Pattern
什么是模式
- An architectural pattern is a package of design decsions that is found repeatedly in practice.
- Has known properties that permit reuse and descrive a class of architecture.
- 三个架构模式:Module pattern, Component-and-connector patterns and Allocation patterns
The definition, concepts, and types of Module Structure, Allocation Structure, and C&C1.Structure.
Module Structure
- definition:
模块结构的基本元素是模块,是实现基本单元。模块表示一种考虑系统代码的方法,被分配功能责任区域。
type:
- 分解:分解的结果是通过“是一个子模块”关系将彼此关联起来的模块,分解展示如何将较大的模块递归地分解为较小的子模块,直到足够小,可以被理解和实现。
- 使用:模块、过程和模块接口上的资源,这些单元通过使用关系连接起来,称第一个单元使用第二个单元。模块结非常适合增量式开发,通过添加模块并通过使用关系连接进系统,实现系统的增量式开发。
- 分层:当以一种特定的方式小地控制该结构的使用关系时,就出现了由层组成的系统。层是相关功能的一致的集合。把下层实现对上层隐藏起来,实现可移植性。
- 类和泛化:模块结构中的模块具体实现为类。
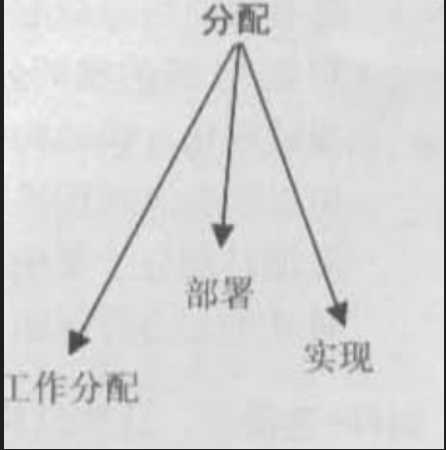
Allocation structure
分类结构:展示软件元素和创建并执行软件的一个或多个外部环境中的元素之间的关系。问答的问题是:每个软件元素在什么处理器上执行?在开发、测试和系统构建期间,每个元素储存在什么文件中?分配给开发小组的软件元素是什么?
type:
- 部署:部署结构展示如何将软件分配给硬件处理和通信元素。元素是软件、硬件实体和通信路径,关系是分配给和移植到。
- 实现:实现结构展示软件元素是如何映射到系统开发、集成或配置控制环境中的文件结构上。
- 工作分配:工作分配结构将实现和集成模块的责任分配给适当的开发小组,可以使关于谁做该工作的决策具有管理上的和架构上的两层含义变得很清晰。
C&C Structure
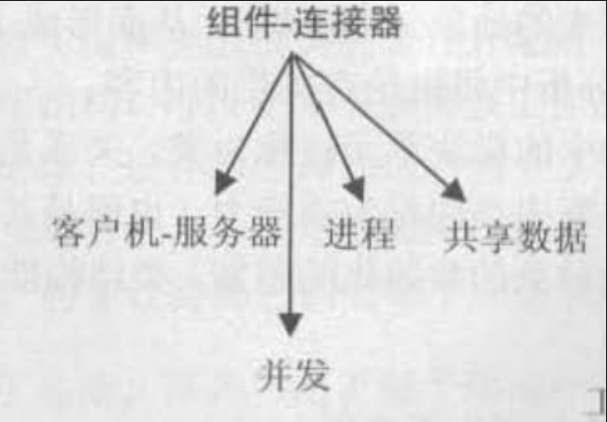
该结构内的基本元素为运行时组件和连接器。该结构可以回答什么是主要执行组件、如何交互、共享数据存储、哪里可以并行运行。
type:
- 进程或通信进程:处理运行系统的动态方面,通过通信、同步和/或排除操作彼此相连的进程是基本单元。
- 并发:单元是组件、连接器是逻辑线程。逻辑线程是一系列的计算,可以将这些计算分配给不同的物理线程单独运行,从而不阻塞当前线程。
- 共享数据或存储库:该结构由创建、储存和访问持久数据的组件和连接器组成。展示软件元素如何产生和使用数据,可以使用该结构确保良好的性能和数据完整性。
- CS架构:系统被构建为一组彼此协作的客户机和服务器。组件是客户机和服务器,连接器是协议以及共享来执行系统工作的消息。
总结:
问题:
- Seven categories of design decisions?
- Allocation of responsibilities / 责任分配
- Coordination model / 协调模型
- Data model / 数据模型
- Management of resources / 资源管理
- Mapping among architectural elements / 架构元素之间的映射
- Binding time decisions / 绑定时间决策
- Choice of technology / 技术选择
- lts role in project risk reduction? (how to reduce risks?).
Software architecture plays a critical role in reducing risks by providing a clear structure that supports system design, development, and evolution. It influences decisions about scalability, maintainability, performance, and security. / 软件架构通过提供支持系统设计、开发和演进的清晰结构,发挥了降低风险的关键作用。它影响了关于可扩展性、可维护性、性能和安全性的决策。
- Decompose Complexity: By breaking down the system into manageable modules or components, you reduce the complexity of individual parts, making the system easier to understand, develop, and maintain. / 分解复杂性:通过将系统分解为可管理的模块或组件,可以减少单个部分的复杂性,使系统更易于理解、开发和维护。
- Design for Change: Designing components with well-defined interfaces and minimal dependencies between them ensures that future changes can be made without affecting other parts of the system. This reduces the risk of costly and time-consuming rework. / 为变更设计:设计具有明确定义接口和最小依赖关系的组件,可以确保未来的变更不会影响系统的其他部分。这降低了昂贵和耗时的重做风险。
- Fault Tolerance and Redundancy: Implementing failover mechanisms and redundant systems in the allocation structure helps ensure that the system remains operational even in the face of hardware failures or unexpected conditions. / 容错和冗余:在分配结构中实现故障转移机制和冗余系统有助于确保系统即使在硬件故障或意外情况下也能保持运行。
- Performance and Scalability: Properly designing how components are distributed and how tasks are allocated across hardware resources ensures that the system can scale efficiently, thus avoiding performance bottlenecks that might cause project delays or cost overruns. / 性能和可扩展性:正确设计组件的分布方式以及如何在硬件资源之间分配任务,可以确保系统能够高效扩展,从而避免可能导致项目延迟或成本超支的性能瓶颈。
- Security Considerations: Architecture decisions that consider security upfront can prevent costly security breaches, reduce vulnerability, and ensure compliance with regulations, ultimately lowering the risk of legal or financial consequences. / 安全考虑:考虑安全性的架构决策可以防止昂贵的安全漏洞,减少漏洞,并确保符合法规,最终降低法律或财务后果的风险。
- Early Prototyping and Validation: Architecture allows teams to build prototypes or models of high-risk components early in the project, which can validate design assumptions and reduce the risk of costly design changes later in the process. / 早期原型和验证:架构允许团队在项目早期构建高风险组件的原型或模型,这可以验证设计假设,并降低后续过程中昂贵设计更改的风险。
- Documentation and Communication: Clear architectural decisions and documentation help align the development team, reducing misunderstandings and rework that could arise from unclear or incomplete design decisions. By incorporating these strategies, the architecture ensures that the system is robust, flexible, and capable of handling change, thereby minimizing risks to the project. / 文档和沟通:清晰的架构决策和文档有助于使开发团队保持一致,减少因不清晰或不完整的设计决策而产生的误解和重做。通过采用这些策略,架构确保系统是强大的、灵活的,并能够处理变化,从而将项目风险降至最低。
下面介绍几个重点模式的具体模式架构
Peer-to-Peer Pattern
p2p解决的问题:将一组地位平等的计算实体分布式地通过一个共同的协议连接在一起,使得它们能够组织和共享服务,具有高可用性和可扩展性。
定义:P2P是一种网络架构,其中每个节点(或称为对等体)都可以作为客户端和服务器,直接与其他节点通信和共享资源,而无需通过集中式服务器。
概念:
- 节点(Peer):网络中的每个参与者。
- 分布式网络:没有中心服务器,所有节点都可以直接相互通信。
- 资源共享:节点可以共享文件、带宽、计算能力等资源。
p2p的通信模式是请求-回复模式,所以对于无连接的udp协议非常合适。
- weaknesses 弱点:
- Managing data consistency, data/service availability, backup, and recovery are all more complex. / 在点对点(P2P)系统中,有效维护数据一致性是一个基本挑战。由于P2P网络的动态性和去中心化特性,保持数据的一致性、可用性、备份和恢复变得更加复杂。
- Small peer-to-peer systems may not be able to achieve quality goals such as performance and availability. / 小型P2P系统可能无法实现性能和可用性等质量目标。这是因为P2P网络的性能和稳定性可能会受到连接对等体数量的影响,大型P2P网络可能会遭受响应时间变慢和延迟增加的影响,影响整体用户体验。
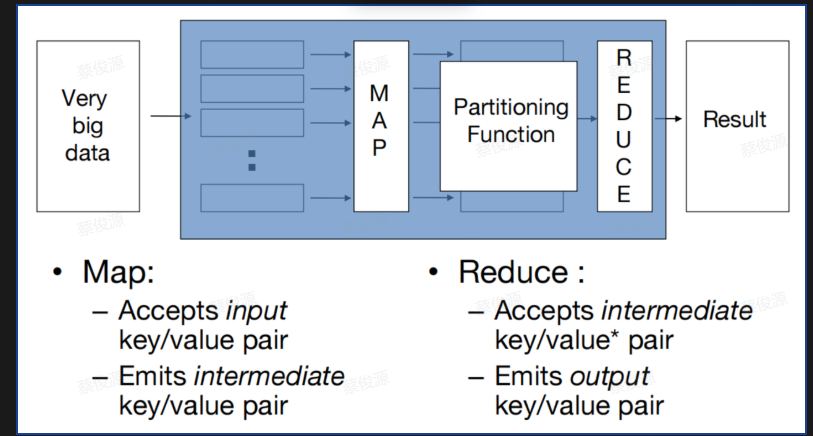
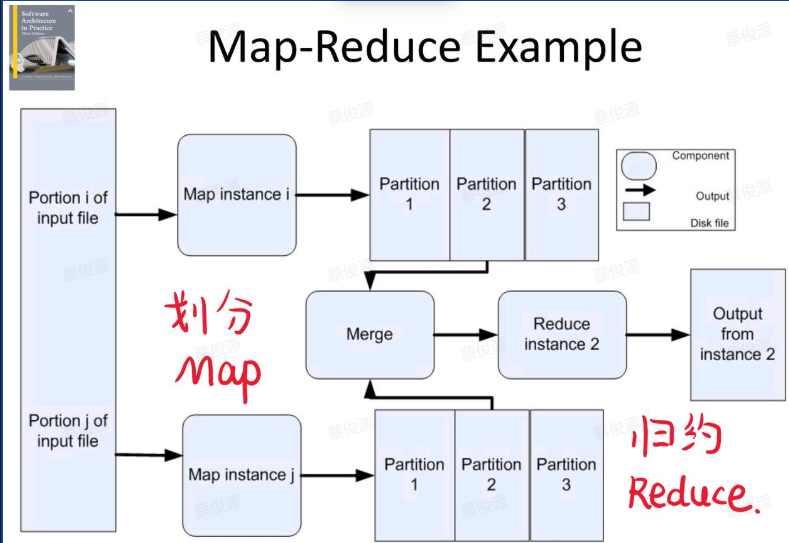
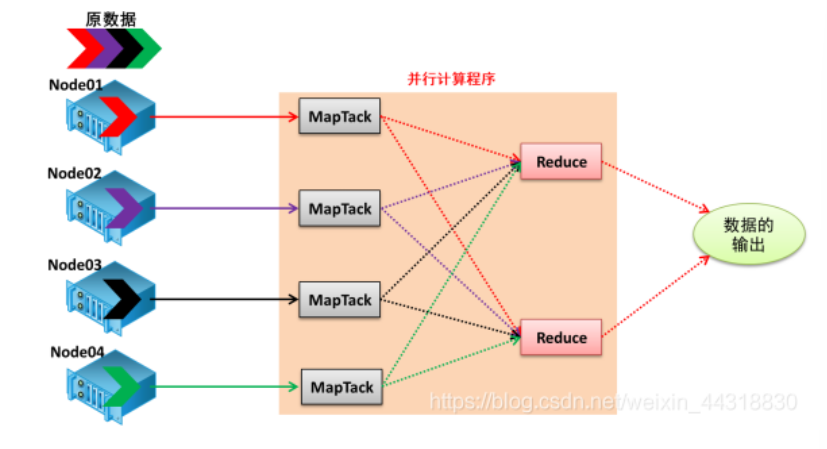
MapReduce Pattern
核心思想:分而治之,先分后合。
定义:MapReduce 是一种编程模型和分布式计算框架,用于在计算集群上处理大规模数据集。最早由 Google 在 2004 年提出,它通过将计算任务分成映射(Map)和归约(Reduce)两个阶段,来高效完成数据的分布式处理,广泛应用于大数据处理平台(如 Hadoop)。
理念:
- Map:将主句进行拆分,把复杂的任务分解为若干简单任务并行处理,可以进行拆分的前提这些任务可以并行计算,彼此间没有依赖关系。
- Reduce:对数据进行汇总,即对map阶段的结果进行全局汇总
Wakeness:
- 高延迟: Shuffle 阶段需要频繁的磁盘 I/O 和网络通信,导致延迟较高。不适合需要多次迭代的算法(如机器学习)。
- 灵活性差: 编程模型固定,对于复杂的数据处理流程(如多步骤的工作流)支持不足。
- 资源利用效率低:任务间的等待和资源浪费(如空闲 CPU 或内存)较为明显。
- 故障恢复代价高:容错机制会导致任务重新执行,增加计算开销。 依赖顺序执行:
Strength:
- 提供强大的容错机制,节点失败时任务会自动重新调度。通过 HDFS 等分布式文件系统实现数据的高可用性。
- 支持横向扩展,可在数千台节点上处理 PB 级别的数据。
- 用户只需专注于实现 Map 和 Reduce 函数,系统负责并行化、分布式调度和容错。
trade off:
Pipe-and-Filter Pattern
- Context: Streaming data processing / 背景:流数据的处理
- Problem: How to speed up data processing? / 问题:如何加快数据处理速度?
- define: Pipe-and-Filter Pattern 是一种架构模式,广泛应用于数据流处理系统中。它将系统的处理逻辑分解为一系列的过滤器(Filters)和管道(Pipes),数据依次通过这些组件进行处理。每个过滤器完成一个独立的处理任务,而管道则负责在过滤器之间传递数据。
- Solution: Data arrives at a filter’s input port, is transformed, and then is passed via its output port through a pipe to the next filter. / 解决方案:数据到达过滤器的输入端口,被转换后,然后通过其输出端口通过管道传递给下一个过滤器。
- A single filter can consume data from, or produce data to, one or more ports. / 单个过滤器可以从一个或多个端口消费数据,或向一个或多个端口产生数据。
- Elements: / 元素:
- Filter, which is a component that transforms data read on its input port to data written on its output port. / 过滤器,这是一个组件,它将其输入端口读取的数据转换为写在其输出端口的数据。
- Pipe, which is a connector that conveys data from a filter’s output port to another filter’s input port. / 管道,这是一个连接器,它将数据从一个过滤器的输出端口传递到另一个过滤器的输入端口。
- Relations: / 关系:
- The attachment relation associates the output of filters with the input of pipes and vice versa. / 连接关系将过滤器的输出与管道的输入以及反之亦然相关联。
- Constraints: / 约束:
- Connected filters must agree on the type of data being passed along the connecting pipe. / 连接的过滤器必须就沿连接管道传递的数据类型达成一致。
Weakness:
- 数据在过滤器之间的传输(尤其是通过文件或网络管道)会引入额外的延迟和开销。
- 各过滤器是独立的模块,错误的传播和调试可能变得复杂。
- 每个过滤器可能对数据格式有特定要求,格式转换可能增加复杂性。
- 对实时性要求较高的系统,可能不适合使用此模式。
Strength:
- 数据流和逻辑处理的分离使系统的架构清晰。
- 过滤器之间低耦合,修改或替换某个过滤器对其他部分的影响较小。
- 易于调整处理逻辑,支持不同的过滤器组合和数据流模式。
- 在多核或分布式环境下,可以显著提高系统性能。
问题:
- P2P’s definition, basic concepts, related QAs (e.g., availability and performance). weaknesses (how to improve?), strengths, and trade-offs.
- mMapReduce 同上
- Pipe-and-Filter 同上
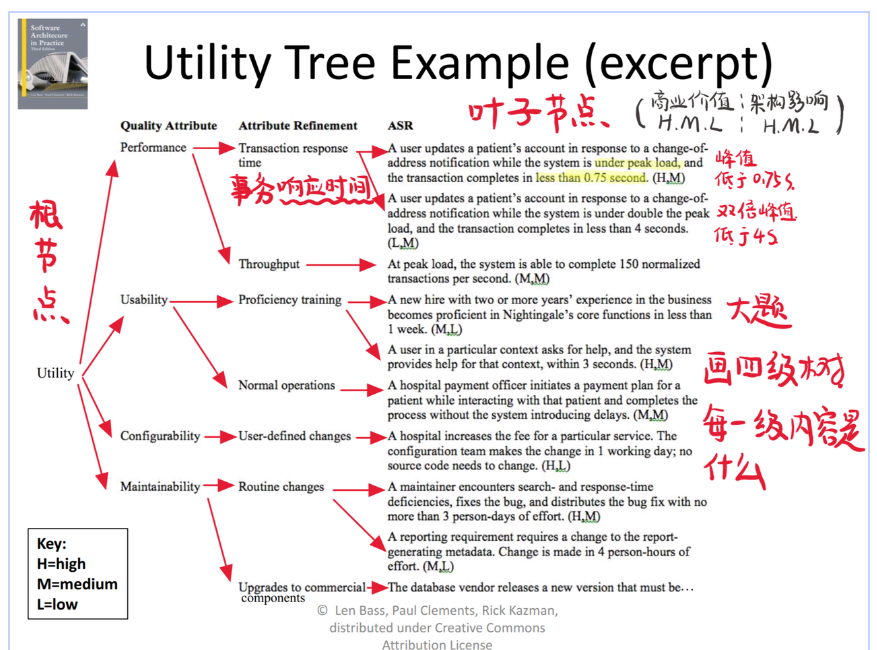
ATAM (architectural reasons), Participants’ Roles, the usage of Utility Tree
ATAM 架构权衡分析方法
Introduction
ATAM的设计使得评估者无需熟悉架构或其商业目标,系统甚至无需已经构建,且可能有大量的利益相关者。
Participants
- The evaluation team
- Project decision makers
- Architecture stakeholders 架构利益相关者
Participants’ Roles
- The evaluation team: 评估团队负责执行 ATAM 评估过程。他们通常由架构评估专家(能力强、公正无私的外部人员)组成,负责引导评估过程,收集和分析数据,并生成评估报告。
- Project decision makers: 项目决策者是那些对项目有决策权的人。他们通常包括项目经理、产品经理和其他高层管理人员。他们的角色是提供项目的业务驱动因素和目标,并根据评估结果做出关键决策。
- Architecture stakeholders: 架构利益相关者是那些对系统架构有兴趣或受其影响的人。这些人可能包括开发人员、测试人员、运维人员、客户和最终用户。他们的角色是提供关于系统需求和约束的信息,并参与讨论和评估架构决策的影响。
Outputs of the ATAM
Primary Outputs of the ATAM
- A set fo risks and nonrisks
- 风险被定义为可能根据质量属性要求导致不良后果的架构决策
- 非风险是被认为安全的架构决策
- A set of risk themes
- 检查所有风险以寻找识别架构中的系统弱点的主题
- 这些风险主题将威胁项目的商业目标
Steps of the ATAM
- Present the ATAM
- Present the business drivers 展示业务驱动因素
- 重要的功能
- 相关的技术、管理、经济或政治限制
- 商业目标和背景
- 主要利益相关者
- 架构驱动因素
- Present the architecture 展示架构
- Identify architectural approaches
- Generate Utility Tree
- Analyze architectural approaches
- Brainstrom and prioritize scenarios
- Analyze the architectural approaches
- Present results
ASR:Architecture significant requirement
在一个系统中质量属性也是有轻重之分的,如何确定一个系统的asr,并架构utility tree,对于系统的设计和评估是非常重要的。
How to find ASR?
- From Requirements Document
- By Interviewing Stakeholders
- a list of architectural drivers
- a set of QA scenarios(质量属性场景) that the stakeholders prioritized
质量属性场景样例(背就完事
Availability / 可用性
1
The heartbeat monitor detects that the server is non-responsive during normal operations. The system informs the operator and continues to operate with no downtime. / 心跳监控器检测到服务器在正常运行期间无响应。系统通知操作员,并继续在没有停机的情况下运行。
- Stimulus: non-responsiveness / 刺激:无响应
- Response: inform the operator / 响应:通知操作员
- Response measure: no downtime, or 100% availability percentage / 响应度量:无停机时间,或100%的可用性百分比
- Environment: normal operation / 环境:正常运行
- Artifact: heartbeat monitor / 工件:心跳监控器
- Stimulus source: server / 刺激源:服务器
Interoperability / 互操作性
- ① Our vehicle information system sends our current location to the traffic monitoring system. 我们的车辆信息系统将当前位置发送到交通监控系统。
- ② The traffic monitoring system combines our location with other information, overlays this information on a Google Map, and broadcasts it. 交通监控系统将我们的位置信息与其他信息结合,并将这些信息叠加在 Google 地图上,然后广播出去。
- ③ Our location information is correctly included with a probability of 99.9%. 我们的位置信息正确包含的概率为 99.9%。
- Source: Our vehicle information system / 我们的车辆信息系统
- Stimulus: A request to exchange information among system(s) / 系统间交换信息的请求
- Artifact: The systems to exchange information among system(s) / 系统间交换信息的系统
- Environment: System(s) wishing to inter-operate are discovered at run time or known prior to run time / 希望互操作的系统在运行时被发现或在运行之前已知
- Response: One or more of the following / 以下之一或多个: The request is (appropriately) accepted and information is exchanged successfully / 请求被(适当地)接受,信息成功交换。
- 车辆信息系统将位置信息发送给交通监控系统,并成功完成交换,交通监控系统成功接收并整合这些信息。 The request is logged by one or more of the involved systems / 请求被一个或多个相关系统记录。
- 请求的信息交换被系统记录和追踪。
- Response Measure: One or more of the following / 以下之一或多个: Percentage of information exchanges correctly processed / 正确信息交换的百分比
- 在此场景中,99.9% of our location information is correctly included / 我们的位置信息正确包含的概率为 99.9%,即信息交换的正确处理率为 99.9%。 Percentage of information exchanges rejected / 被拒绝的信息交换的百分比
- 根据场景,未提及被拒绝的交换,因此可以假设该百分比为 0。
Modifiability / 可修改性
The developer wishes to change the user interface by modifying the code at design time. The modifications are made with no side effects within three hours. 开发者希望通过在设计时修改代码来更改用户界面。修改在三小时内完成,并且没有副作用。
- Stimulus: Wishes to change UI 刺激: 希望更改用户界面
- Artifact: Code 工件: 代码
- Environment: Design time
- 环境:设计时
- Response: Change made
- 响应:已完成更改
- Response measure: No side effects in three hours
- 响应度量:三小时内无副作用
- Source: Developer
- 来源:开发者
Performance / 性能
Users initiate transactions under normal operations. The system processes the transactions with an average latency of two seconds. 用户在正常操作下发起交易。系统以平均两秒的延迟处理交易。
- Stimulus: Transaction arrivals
- 刺激:交易到达
- Source: Users
- 来源:用户
- Artifact: The system
- 工件:系统
- Response: Process the transactions
- 响应:处理交易
- Response measure / Average latency of two seconds 平均延迟为两秒
- 响应度量:
- Environment / 环境: Under normal operation 正常操作下
Security / 安全性
A disgruntled employee from a remote location attempts to modify the pay rate table during normal operations. The system maintains an audit trail and the correct data is restored within a day. 一名不满的员工从远程位置试图在正常操作期间修改工资表。系统保持审计记录,并在一天内恢复正确的数据。
- Stimulus: unauthorized attempts to modify the pay rate table 刺激:未授权的尝试修改工资表
- Stimulus source: a disgruntled employee 刺激源:一名不满的员工
- Artifact: the system with pay rate table 工件:包含工资表的系统
- Environment: during normal operation 环境:正常操作期间
- Response: maintains an audit trail 响应:保持审计记录
- Response measure: correct data is restored within a day 响应度量:在一天内恢复正确的数据
Testability / 可测试性
The unit tester completes a code unit during development and performs a test sequence whose results are captured and that gives 85% path coverage within 3 hours of testing. 单元测试员在开发过程中完成一个代码单元,并执行一个测试序列,捕获其结果,并在 3 小时的测试内达到 85% 的路径覆盖率。
- Source / 来源:
- Unit tester 单元测试员
- Stimulus / 刺激:
- Code unit completed 代码单元完成
- Artifact / 工件:
- Code unit 代码单元
- Environment / 环境:
- Development 开发环境
- Response / 响应:
- Capture results 捕获结果
- Response measure / 响应度量:
- 85% path coverage in three hours 在三小时内达到 85% 的路径覆盖率
Usability / 易用性
The user downloads a new application and is using it productively after two minutes of experimentation. 用户下载一个新应用程序,并在两分钟的试验后开始高效使用它。
- Source / 来源:
- User 用户
- Stimulus / 刺激:
- Download a new application 下载新应用程序
- Artifact / 工件:
- System 系统
- Environment / 环境:
- Runtime 运行时
- Response / 响应:
- User uses application productively 用户高效使用应用程序
- Response measure / 响应度量:
- Within two minutes of experimentation 在两分钟的试验内
From https://a1npn29y3xu.feishu.cn/wiki/Kxggw6yRZixCWIkbdsfcW2Pcn3f
By Understanding the Business Goals QAW
In Utility Tree (必考)
ASR必须满足以下特性:
- 对架构有深远影响
- 具有高商业或任务价值
Utility Tree 效用树
定义
A way to record ASRs all in one place.
- root node(utility):表示系统的整体目标(system qualifications)
- sub node:表示具体的质量属性(性能、可扩展性、可用性等),叫树的第二层,包含广泛的质量属性类别
- sub node:叫树的第三层,细化这些类别
- leaf node:表示这些质量属性的具体场景或测试用例
Open discussion.
- 例子:
- The abstract common services tactic is intended to reduce coupling, but it alsomight reduce cohesion?
- Discuss the choice of programming language
(an example of choice of technology)and its relation to architecture in general
TestBook p409
真题
Which of the following should be included in the consideration of a Allocation Structure? C A. What are the major executing components and how do they interact at runtime B. what part of the system can run in parallel C. How software is assigned to hardware processing and communication elements. D. How does data process through the system
Which one of the following structures pertains to the C&C Structure? A. Service structure A B. Class structure C. Deployment structure D. Decomposition structure
- Which one of the following tactics is for improving the modifiability? C A. Removal from Service B. Detect service attack C. Increase Semantic Coherence D. Active redundancy
“A User asks for help, and the system provides help for that context” is a scenario of . B A. Security B. Usability C. Performance D. Availability
Which of the following descriptions about the relationships between Architectural Pattern and Architectural tactic is True? A A. Pattern have to be augmented with tactics for the design of real systems B. If a tactic has side effect, it should not be added into the design of a system C. Tactics are simpler than patterns D. Tactics are built from Patterns
Boehm and Turner found that projects have a “sweet spot” where up-front architecture planning pays off. For the ( B ),the sweet spot is around 40% of the project schedule. A. 10KSLOC project B. 100KSLOC project C. 1000KSLOC project D. extremely large projects with very stable requirements
The ( D ) is focused on system-level concerns and specifically the role that software will play in the system and it is keenly dependent on the participation of system stakeholders. A. Utility Tree B. Quality Attribute Workshop C. Attribute Driven Design D. Architecture Trade-off Analysis Method
The testability tactics of“ ( A )” refers to isolating an instance of the system from the real world to enable experimentation that is unconstrained by the worry about having to undo the consequences of the experiment. A. Sandbox B. Executable Assertions C. Abstract Data Sources D. Localize State Storage
Availability tactics are designed to enable a system to endure system faults so that a service being delivered by the system remains complaint with its specification. A fault happens when the following stimuli occur EXCEPT FOR ( D ) A. Omission: A component fails to respond to an input B. Crash:The component repeatedly suffers omission faults C. Timing: A component responds but the response is early or late. D. Event arrivals: The stimuli arrive either from external or internal sources.
- Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE about the CAP theorem? A A. According to CAP theorem, it is possible to achieve Consistency, Availability and Partition simultaneously (同时地). B. The CAP theorem is about the three important properties, which are Consistency, Availability and Partition, of a distributed system managing shared data. C. According to CAP theorem, one of the the three important properties, Consistency, Availability and Partition, should be sacrificed.
D. For many applications, it is a choice to sacrifice consistency and provide immediate availability and eventually consistency.